Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9410 94-262, 120 Pages, 1994/09
This study clarified the tensie properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 2.25Cr-1Mo and SUS321 steels at ultra-high temperature up to 1,200 C which will be used in analysys and evaluation of the tube burst in steam generators of fast breeder reaetors. (1)Tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 2.25Cr-1Mo and SUS321 steels at 1,200
C which will be used in analysys and evaluation of the tube burst in steam generators of fast breeder reaetors. (1)Tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 2.25Cr-1Mo and SUS321 steels at 1,200 C were 2.5, 2,and 2.5kg/mm
C were 2.5, 2,and 2.5kg/mm , respectively. (2)The difference for tensile strength and 0.2% yeild strength between specimen heat rate and heat holding time could not be found in the present. (3)The temperatures of the tube burst at the maximum internal pressure of 150kg/cm
, respectively. (2)The difference for tensile strength and 0.2% yeild strength between specimen heat rate and heat holding time could not be found in the present. (3)The temperatures of the tube burst at the maximum internal pressure of 150kg/cm corresponding to the practical use condition were expected to be approximately 960
corresponding to the practical use condition were expected to be approximately 960 C for Mod.9Cr-1M0, 860
C for Mod.9Cr-1M0, 860 C for 2.25Cr-1Mo and 1040
C for 2.25Cr-1Mo and 1040 C for SUS321, respectively. These tests result will be reflected to evaluation of tube burst by sodium water reaction.
C for SUS321, respectively. These tests result will be reflected to evaluation of tube burst by sodium water reaction.
; *; ; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9410 94-261, 143 Pages, 1994/06
In this study, tensile, creep and relaxation test in air were performed in order to examine the mechanical properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel which is a candidate material for once throuth type steam generator of large scale fast breeder reactor. Tested materials were plate(12mmt) simulating heat exchenger tube and heat exchenger tube of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel and 9Cr-2Mo steel was also tested as reference material. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)Tensile properties (a)Ultimate tensile strength and 0.2% yield strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels were higher than the tentative Su and Sy values of the design allowable stress in the test temperature below 600 C. (b)Ultimate tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels plate and tube were higher than that of 9Cr-2Mo Steels. (3)The difference in ultimate tensile strength and 0.2% yield strength between steel plate and tube could not be found in these tests. (2)Creep properties (a)Creep rupture strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel plate and tube was higher than the tentative S
C. (b)Ultimate tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels plate and tube were higher than that of 9Cr-2Mo Steels. (3)The difference in ultimate tensile strength and 0.2% yield strength between steel plate and tube could not be found in these tests. (2)Creep properties (a)Creep rupture strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel plate and tube was higher than the tentative S value of the design creep-rupture stress intensity at 500
value of the design creep-rupture stress intensity at 500 600
600 C, and this tendency is significant in the range of longer rupture time. (b)For the relation between steady creep rate and creep rupture time, steady creep rates obtained in this study coincided well with the
C, and this tendency is significant in the range of longer rupture time. (b)For the relation between steady creep rate and creep rupture time, steady creep rates obtained in this study coincided well with the 
 of tentative creep strain equation. (c)Creep rupture strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel plate and tube was higher than that of 9Cr-2Mo steel. (3)Relaxation properties (a)In the strain range of 0.1
of tentative creep strain equation. (c)Creep rupture strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel plate and tube was higher than that of 9Cr-2Mo steel. (3)Relaxation properties (a)In the strain range of 0.1 0.5%, stress rapidly relaxed during the short hold time, and stress relaxation tended to be saturate beyond 50hours. These relaxation stresses became large in higher temperature and higher strain level. (b)Stress relaxation behavior was predicted approximately by tentative creep equation of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. The analysis of these test results is continued to develop of evaluation method of material strength.
0.5%, stress rapidly relaxed during the short hold time, and stress relaxation tended to be saturate beyond 50hours. These relaxation stresses became large in higher temperature and higher strain level. (b)Stress relaxation behavior was predicted approximately by tentative creep equation of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. The analysis of these test results is continued to develop of evaluation method of material strength.
Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tanabe, Hiromi; Usami, Masayuki
PNC TN9410 93-212, 134 Pages, 1993/09
A one-through unit type steam generator (SG) having the Mod.9Cr-1MO Steel for its heat transfer tube is considered to be promising for the development of large FBR SGs. Wastage data of the tube material was already obtained for the micro-/small leak region as formerly reported. Therefore, intermediate leak wastage tests were conducted in the range from 10 g/s to around 200 g/s by using the SWAT-1 test facility and the test results are summarized as follows: (1)The wastage resistivity of the Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel is between that of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel and austenitic stainless steel; namely, the Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel has about half the of wastage rate of the 2.25Cr-1Mo steel. An experimental wastage formula in the intermediate leak region was derived from the test data. (2)Almost all of the wastage profile of target tubes was toroidal type and it became about half the cross section area of the 2.25Cr-1Mo steel. An experimental formula on initial leak diameters versus equivalent secondary failure diameters was derived in the intermediate leak region. These test results would be applied to failure propagation analysis code LBAP which is to be used for the design of a one-through unit type SG.
; ; *; *; *; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9450 91-010, 259 Pages, 1991/10
In order to advancement in materials strength standard on elevated temperature design guide of the FBRs and evaluation method of materials strength behavior, this report are presented about the creep properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels for steam generator, based on the R&D results obtained through the activities of material tests. Contents of the data sheet are as follows; Material : Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels (Base Metal) Plate 7 Heats (F2, F6, F7, F9, F10, NSC1, NSC2) Forging 8 Heats (F4, F5, F8, F11, VIM, ESR, F520, F550) Tube 1 Heats (F3) Test temperature : 450 650
650 C Test method : According to JIS and FBR Metallic Materials Test Method Test environment : In Air and in Sodium Number of deta : 314 points
C Test method : According to JIS and FBR Metallic Materials Test Method Test environment : In Air and in Sodium Number of deta : 314 points
; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; *; *; *; *
PNC TN9450 91-004, 71 Pages, 1991/07
In order to advancement in materials strength standard on elevated temperature design guide of the FBRs and evaluation method of materials strength behavior, this report are presented about the low-cycle fatigue properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel, based on the R&D results obtained through the sctivities of material tests. Contents of the data sheet are as follows; [Material ; Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel(SR)] F2 Heat 1,000 1,000
1,000 12mm
12mm (Plate) F4 Heat 1,000
(Plate) F4 Heat 1,000 1,000
1,000 250mm
250mm (Forging) F6 Heat 1,000
(Forging) F6 Heat 1,000 1,000
1,000 25mm
25mm (Plate) [Environment; In Air and in Sodium] [Test temperature ; 450, 500, 550, 600 and 650
(Plate) [Environment; In Air and in Sodium] [Test temperature ; 450, 500, 550, 600 and 650 C] [Strain rate ; 0.1%/sec (10
C] [Strain rate ; 0.1%/sec (10 mm/mm/sec)] [Strain range ; 0.38%
mm/mm/sec)] [Strain range ; 0.38%  1.86%] [Number of deta ; 83 points]
1.86%] [Number of deta ; 83 points]
 280mm t)
280mm t); ; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9410 91-099, 106 Pages, 1991/02
This stady was performed in order to confirm the influence of sampling method on Creep properties of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings which are promising as candidate materials for steam generator of large scale fast breeder reactor. This results are to be reflected on fundation of materials strength standard. Test materials are four kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings (thickness:250 280mmt) such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8 heats), 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V(G3 heat), 9Cr-2Mo (H6 heat) steels. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)In order to evaluation of fundamental material properties, creep-rupture data on three kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 9Cr-2Mo and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steels was obtained up to 10,000 hours. (2)The Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel exhibited most excellent creep-rupture strength and the 9Cr-2Mo steel was the worst among the three. (3)The effect of the sampling location of specimens on creep strength was not significant for Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. But for 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel and 9Cr-2Mo steel, longer creep rupture time was observed with spcimens taken from just below the center of the surface with direction of L, and shorter creep rupture time was observed for those taken from t/2 thickness at the center with direction of Z. (4)Creep strength of 9Cr-2Mo steel was lower than that of Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8)and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel. But rupture elongation and reduction of area of 9Cr-2Mo steel was greater than hat of other three materials, irrespective of the sampling location of specimens.
280mmt) such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8 heats), 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V(G3 heat), 9Cr-2Mo (H6 heat) steels. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)In order to evaluation of fundamental material properties, creep-rupture data on three kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 9Cr-2Mo and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steels was obtained up to 10,000 hours. (2)The Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel exhibited most excellent creep-rupture strength and the 9Cr-2Mo steel was the worst among the three. (3)The effect of the sampling location of specimens on creep strength was not significant for Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. But for 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel and 9Cr-2Mo steel, longer creep rupture time was observed with spcimens taken from just below the center of the surface with direction of L, and shorter creep rupture time was observed for those taken from t/2 thickness at the center with direction of Z. (4)Creep strength of 9Cr-2Mo steel was lower than that of Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8)and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel. But rupture elongation and reduction of area of 9Cr-2Mo steel was greater than hat of other three materials, irrespective of the sampling location of specimens.
 280mmt).
280mmt).*
PNC TN9410 90-122, 58 Pages, 1990/06
This study was performed to examine the tensile properties of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings, which are promising as the candidate materials for steam generator of large scale fast breeder reactor the influence of thermal aging and sampling location/direction. These results are to be reflected on fundation of materials strength standard. Test materials are three kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings (thichiness:250 280mmt) such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4,F8 heats), 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V(G3 hrats), 9Cr-2Mo (H6 heats) steels. The heat treatment on the thermal aging were carried out at 500, 550
280mmt) such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4,F8 heats), 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V(G3 hrats), 9Cr-2Mo (H6 heats) steels. The heat treatment on the thermal aging were carried out at 500, 550 C for 3000hours. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)Tensile properties were much about the same between Mod.9Cr-1Mo and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V Steel forgings. (2)Tensile strength of four materials at direction Z was slightly lower than that of direction L or C and there are no significant diffrence on the sampling location/direction. (3)Tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel forgings after thermal aging for 3000hours was same as that of as-received ones. However, the strength of 9Cr-2Mo steel forging at high temperature dicreased because of aging effect. (4)The 0.2 percent yield stress and tensile strength of forged steels satisfied the PNC preliminary design standard values of Sy and Su, but inferior to plating and tubing steels. However, tensile strengh of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel forging (F8 heat) at the lower temperature than 400
C for 3000hours. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)Tensile properties were much about the same between Mod.9Cr-1Mo and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V Steel forgings. (2)Tensile strength of four materials at direction Z was slightly lower than that of direction L or C and there are no significant diffrence on the sampling location/direction. (3)Tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel forgings after thermal aging for 3000hours was same as that of as-received ones. However, the strength of 9Cr-2Mo steel forging at high temperature dicreased because of aging effect. (4)The 0.2 percent yield stress and tensile strength of forged steels satisfied the PNC preliminary design standard values of Sy and Su, but inferior to plating and tubing steels. However, tensile strengh of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel forging (F8 heat) at the lower temperature than 400 C and 9Cr-2Mo steel forging after thermal aging were lower than that of preliminary values. These results were reflected to advance the specification of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel thick forgings.
C and 9Cr-2Mo steel forging after thermal aging were lower than that of preliminary values. These results were reflected to advance the specification of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel thick forgings.
*
PNC TN9410 90-094, 80 Pages, 1990/06
It is needed for FBR design to know physical properties of the structural materials that will be used for FBR-reactor vessels, -steam generators, and -pipes. In this report, six types of steels that are noted as the structural materials for next steps of FBR are taken up. The six types of steels are as follows ; [SUS 304] [SUS 316 (conventional)] [FBR grade SUS316] [SUS321] [2.25Cr-1Mo steel] [Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel (ASTM A387-91).] Physical properties of the steels are measured on rolled plates made by mills. The measured physical properties are as follows ; [Specific gravity] [Specific heat] [Thermal conductivity] [Thermal expansion] [Young's modulus] [Poisson's ratio.] And also the same kinds of physical properties of S.R. (Stess Relieving) heat treated 2.25Cr-1Mo and Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel plates are measured. Measurement of the physical properties of forgings, pipes, and weld metals of selected types of steels of them will be also carried out in 1990 and all summarized data that will contain the results of this report will be used to determin the criteria design values of the physical properties for the next steps of FBR. (Caution) This report only shows the measurement results of the physical properties of the rolled steel plates but doesn't give the design standards of the physical properties for the next steps of FBR.
*; *; Kano, Shigeki; *; *; *; *
PNC TN9410 89-096, 105 Pages, 1989/05
A series of high temperature fracture toughness tests of 9Cr type steel was put in practice on a three-year scheme in 1988, In this experimental study, Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel, 9Cr-2Mo steel and TEMPALOY SW-9(9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V) steel are tested, and fracture toughness (J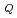 ) of base metal (As-received, SR-treated, Aged) and weldment (weld metal, HAZ) of these three types of steel are investigated. In a first year, fracture toughness tests of base metal (As-received, SR-treated) of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were carried out at RT, 400
) of base metal (As-received, SR-treated, Aged) and weldment (weld metal, HAZ) of these three types of steel are investigated. In a first year, fracture toughness tests of base metal (As-received, SR-treated) of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were carried out at RT, 400 C, 500
C, 500 C, 550
C, 550 C and 600
C and 600 C, respectively. In this report, the test results in the first year are shown. Fracture toughness tests were performed using R-curve method and unloading compliance method according to ASTM E813. The fracture toughness value was the lowest at 400
C, respectively. In this report, the test results in the first year are shown. Fracture toughness tests were performed using R-curve method and unloading compliance method according to ASTM E813. The fracture toughness value was the lowest at 400 C. Even at 400
C. Even at 400 C, however, Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel showed enough high fracture toughness (J
C, however, Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel showed enough high fracture toughness (J
 350kJ/m
350kJ/m ), In the fracture toughness test, tearing modurous T
), In the fracture toughness test, tearing modurous T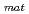 was also measured.
was also measured.